Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
What are Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)?
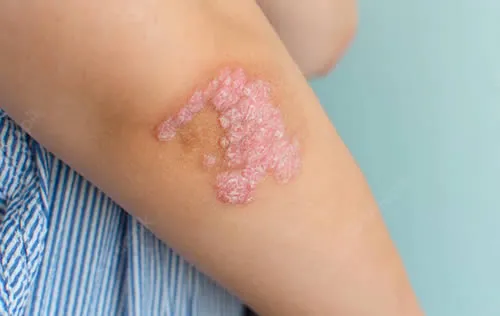
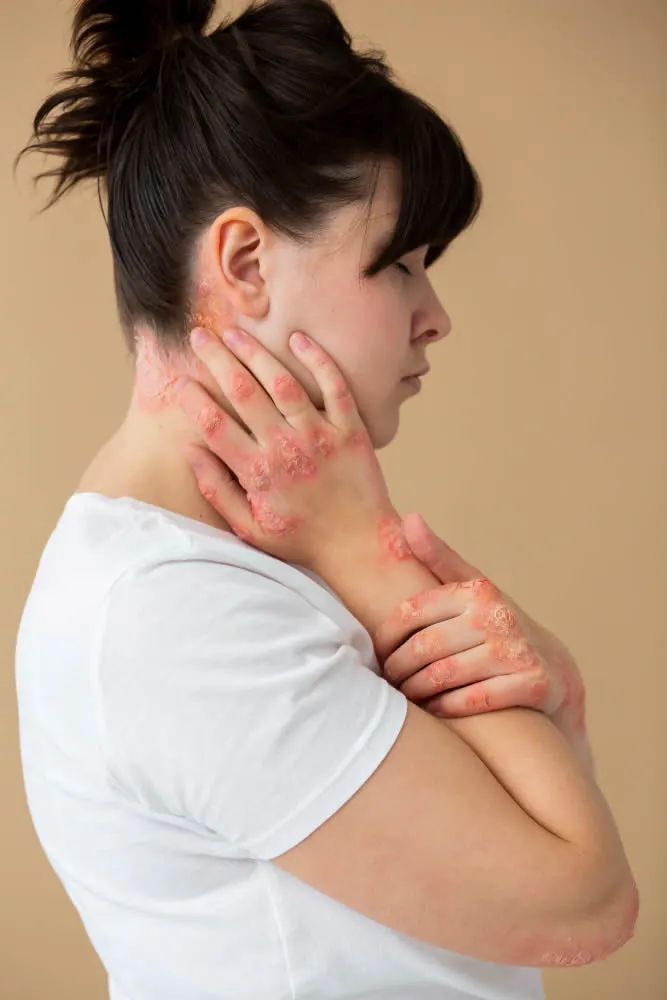
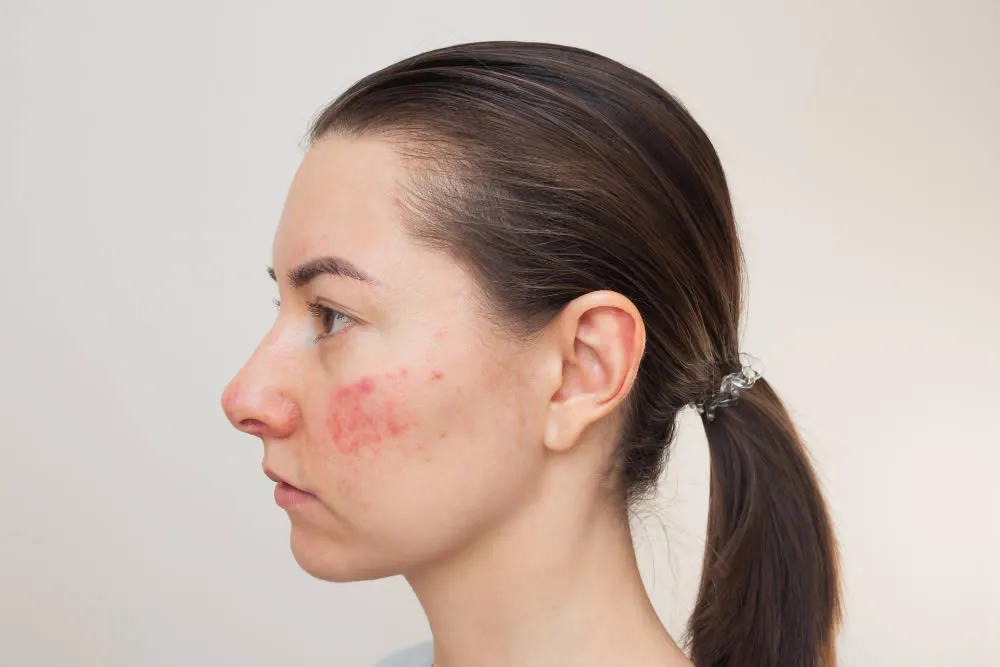
Ringworm is a fungal skin infection that affects the top layer of the skin and causes a circular, ring-shaped rash. The medical name for ringworm is Tinea Corporis, which refers to ringworm of the body. The rash can be itchy and can spread to other areas if not treated. Ringworm is a common and highly contagious skin condition that can be treated with antifungal medication.

What are the causes of Ringworm?
Ringworm is caused by a fungal infection. There are several species of fungi that can cause ringworm, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can infect the skin through direct contact with contaminated surfaces, animals, or other people. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are at higher risk for developing ringworm. Additionally, poor hygiene, sweating, and wearing tight clothing can also increase the risk of getting ringworm.
What are the symptoms of Ringworm?
- Rash: A round, red, and itchy rash that may be scaly, bumpy, or blistery.
- Ring-shaped lesion: The rash forms a ring-like shape, which is why the condition is called “ringworm.”
- Itching: The affected skin may be itchy and may become more itchy at night.
- Blisters: In some cases, blisters may form on the rash.
- Loss of hair: If the scalp is affected, hair may fall out in patches.
It is important to note that some people with ringworm may not experience any symptoms. If you think you may have ringworm, it is best to see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
What treatments are available for Ringworm?
The following treatments are commonly used for ringworm:
- Topical antifungal medications: Over-the-counter creams and ointments, such as clotrimazole and terbinafine, can be applied directly to the affected skin to treat ringworm.
- Oral antifungal medications: If the infection is severe or widespread, a doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medications, such as itraconazole or fluconazole.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, if a bacterial infection has developed in addition to the fungal infection, antibiotics may be necessary to treat the ringworm.
It is important to follow the instructions of the dermatologist or pharmacist when using any of these medications. Treatment typically lasts for several weeks and it is important to complete the entire course of treatment to ensure that the infection is fully treated. In some cases, the ringworm may return after treatment, so it is important to monitor your skin and seek medical attention if necessary.

How to Help Prevent Ringworm?
To help prevent ringworm, you can follow these steps:
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and keep your skin clean.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Don’t share towels, brushes, combs, and other personal items that come into contact with your skin.
- Keep your skin dry: Keep your skin dry, especially after exercising or sweating, as moisture can help the fungus grow.
- Wear appropriate clothing: Wear clothing that covers your skin, especially in warm and humid environments.
- Avoid contact with infected people or animals: If you come into contact with someone or an animal with ringworm, wash your hands thoroughly.
- Clean contaminated surfaces: Clean surfaces that may be contaminated with ringworm, such as gym equipment, with a disinfectant.
- Keep your living environment clean and dry: Make sure your home is clean and well-ventilated to prevent the growth of fungal organisms.
FAQ About Ringworm
How is ringworm transmitted?
Ringworm can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
How long does it take for ringworm to go away?
The length of time it takes for ringworm to go away varies, but most cases can be treated within 4 to 6 weeks.
Can ringworm be prevented?
Yes, practicing good hygiene and avoiding direct contact with infected people or animals can help prevent the spread of ringworm.
Is ringworm contagious?
Yes, ringworm is highly contagious and can be easily spread through direct contact or contaminated surfaces.
Can ringworm spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, ringworm can spread from one part of the body to another if the affected area is not properly treated and covered.
What should I do if I think I have ringworm?
If you suspect you have ringworm, it’s important to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Are there any home remedies for ringworm?
While some home remedies may help relieve the symptoms of ringworm, it’s important to seek medical treatment for proper and effective treatment. Over-the-counter creams or ointments may provide temporary relief, but they do not cure the infection.
Is there a dermatologist near me in Omaha that offers treatment for ringworm?
Yes. At our Omaha dermatology office we offers treatment for Ringworm to patients from Omaha and the surrounding area. Contact our office today to schedule an appointment.